Monday 04.03.23
A Comprehensive Toolbox for Sustainable Tourism Planning and Recovery: Reflections on the Way Forward from Sharm El Sheikh at COP27
Navigating Sustainable Tourism Practices in a Post-COVID World through Integrated Frameworks, Tools, and Capacity Building
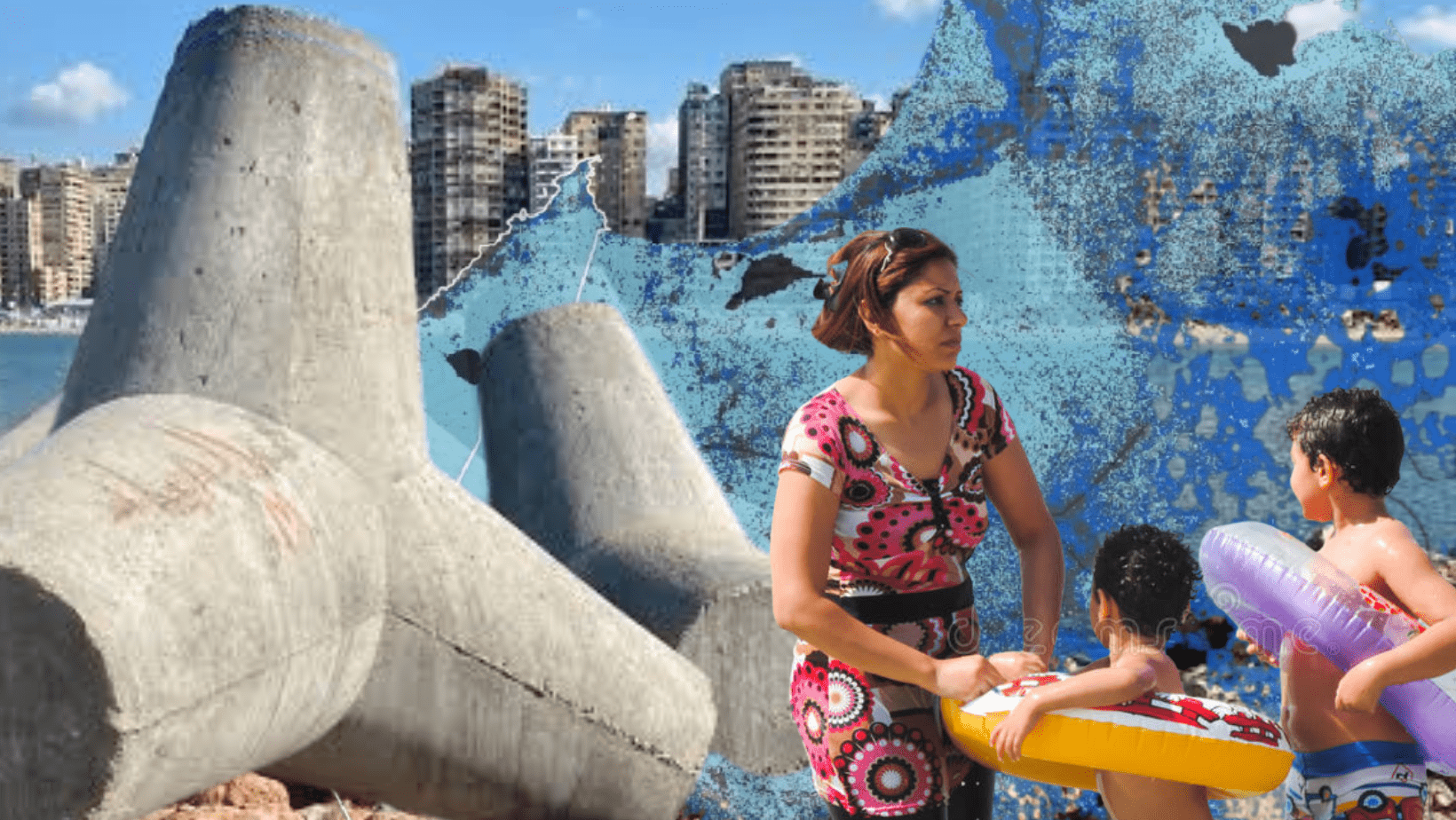
OHK participated in the 2022 United Nations Climate Change Conference, also known as COP27, held in Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt from November 6-20, 2022. The conference was attended by over 92 heads of state and around 35,000 representatives from 190 countries. COP27 served as a platform for governments to negotiate and agree on policies focused on limiting and adapting to the impacts of climate change. Artwork © OHK Consultants.
In 2005, OHK completed a sustainable tourism strategy for Sharm El Sheikh, a popular Egyptian tourist destination renowned for its picturesque beaches and vibrant coral reefs. Seventeen years later, in 2022, Sharm El Sheikh served as the venue for COP27, a significant event in the global fight against climate change that brought together world leaders, experts, and activists to discuss and implement climate action strategies. As OHK returned to this famous destination to attend the conference, it was crucial to reflect on the region's tourism growth and the recovery of this vital sector, which, before the COVID pandemic, made substantial contributions to the global economy.
Tourism's pre-COVID contributions were remarkable, with the industry accounting for 10.4% of global GDP and supporting 1 in 10 jobs worldwide. Furthermore, international tourist arrivals reached 1.5 billion in 2019, highlighting the sector's importance and the need for sustainable practices. The growth of tourism in Sharm El Sheikh has been significant, and the city has become a symbol of Egypt's commitment to sustainable tourism. Sharm El Sheikh and the wider Red Sea region have successfully implemented OHK's sustainable tourism strategy, resulting in improved environmental conservation, economic growth, and increased industry awareness. The city's efforts have led to the conservation of its coral reefs, the expansion of eco-tourism projects across the Sinai Peninsula and the Red Sea coastline, and the reduction of its carbon footprint through various hotel resource efficiency schemes. These initiatives have not only made Sharm El Sheikh a leader in sustainable tourism but have also contributed to the momentum towards addressing global challenges such as climate change and the COVID-19 pandemic.
Amidst the ongoing challenges posed by climate change and the COVID-19 pandemic, Sharm El Sheikh had the honor of hosting COP27, shining a spotlight on how tourist destinations worldwide can inspire and adopt sustainable practices. As OHK reflects on the success of its sustainable tourism strategy for Sharm El Sheikh and the city's remarkable transformation over the years, we recognize that there is still much to be done to establish a common understanding around necessary actions in tourism.
Despite attending various sessions during COP27 and witnessing promising momentum, OHK realizes that achieving a global consensus on sustainable tourism practices remains a challenging task. Navigating the vast array of information and guidelines available can be overwhelming for decision-makers and tourism managers. With hundreds of sources from around the world, the task of comprehending and implementing effective sustainable tourism practices can be daunting.
Recognizing this, OHK envisaged that developing a toolbox for tourism planning and recovery is essential, particularly given the two key factors currently at play.
Firstly, the plethora of frameworks and guidelines issued in recent years for sustainable tourism practices and climate change mitigation has created a complex landscape for stakeholders. A step-by-step approach to examining destinations and addressing climate change issues would require those in the tourism industry tasked with resilience planning to sift through hundreds of sources from across the globe. The impact of COVID has made the development of a toolbox for tourism planning and recovery particularly timely and crucial. By creating a comprehensive and accessible toolbox, OHK aims to simplify this process.
Secondly, it is highly likely that some predictions for the impacts of climate change have been exceeded. Although predicting impacts with complete accuracy is challenging, numerous studies and reports suggest that the potential for more severe and rapid changes is greater than previously anticipated. For instance, some studies suggest that the rate of sea-level rise is accelerating faster than earlier predictions, which could result in more frequent and severe flooding in coastal regions. Furthermore, recent extreme weather events like heatwaves, wildfires, and hurricanes have been linked to climate change, indicating that the impacts may be happening more quickly and with greater intensity than anticipated. As a result, predictions are constantly evolving, and it is essential to have a well-conceived response plan that is clear, concise, well-integrated, and based on a coherent and well-thought-out framework.
OHK has analyzed, synthesized, and integrated the core elements of nearly ten existing frameworks developed by international organizations involved in climate action, creating a cohesive and comprehensive global framework that captures the essence of sustainable tourism planning and recovery. By combining these frameworks, OHK proposes a global framework that is adaptable, relevant, and capable of addressing the diverse range of tourism destinations worldwide. The frameworks include the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) Recovery Guidelines, the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) Tourism Recovery Technical Assistance Package, the Destination Stewardship Center (DSC) Recovery Framework, and the Future of Tourism Coalition Principles for a Responsible Recovery.
OHK has skillfully integrated these frameworks by identifying the complementary aspects and synergies between their various building blocks to create a global framework that highlights the importance of stakeholder engagement, policy development, capacity building, climate change adaptation, and mitigation efforts. Additionally, the framework incorporates the need for investment opportunities, human capital development, integrated spatial planning, and community-based development.
Egypt is facing significant challenges due to climate change, which threaten its economy, food security, and the health and well-being of its citizens. Although Egypt is responsible for only 0.6 percent of global CO2 emissions yearly, the country is highly vulnerable to climate change, including heatwaves, sea-level rise, soil salinization, rainfall retention, and desertification. The Nile Delta is one of the world's top three most vulnerable regions, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). If sea levels rise by 1 meter, 20% of the Delta's land area, including Alexandria, could be submerged, but this is a mild scenario. In an extreme scenario, projections anticipate a 3-meter rise in sea level, which could displace up to 80% of the population. The sea-level rise projections for 2100 are illustrated in dark blue patterns for the extreme scenario, while light blue patterns show a 1-meter rise. The salinization of land and water resources is also expected to significantly impact agriculture, fishing, and freshwater availability. Various projections estimate agricultural production to decrease by 8-47% by 2060, leading to reductions in agricultural employment of up to 39%, while food prices can increase by 16-68%. Egypt is investing significantly in coastal defense structures and integrated coastal management plans to mitigate these impacts. Artwork © OHK Consultants. The projections illustration is courtesy of Climate Central.
The integration of these frameworks offers a more robust approach to sustainable tourism planning and recovery by providing destinations with a comprehensive understanding of the tourism sector's current state and future potential. By recognizing the need for a holistic approach to sustainable tourism, OHK's global framework enables destinations to address key challenges and opportunities in a systematic and coordinated manner. This comprehensive strategy serves as a guide for destinations seeking to develop their own sustainable tourism strategies, ensuring that they are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of the global tourism landscape.
Lebanon is facing several challenges, including an economic crisis, the repercussions of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the Port of Beirut explosion. In addition to these problems, climate change is expected to cause a 14% fall in Lebanon's GDP by 2040, which will increase to 32% by 2080. The Global Carbon Project (GCP) published a report prepared by over 70 scientists at COP27, estimating that global greenhouse gas emissions will rise by 1% in 2022, indicating that current actions have been insufficient. According to experts at Climate Action Tracker (CAT), world temperatures could rise 2.7°C above pre-industrial levels by 2100. In the worst-case scenario where emissions keep increasing, Lebanon and other countries could experience a temperature increase of over 2°C as early as 2035. These climate impacts will also lead to scarcer water resources, negatively impacting agricultural output and the livelihoods of many communities. Additionally, Lebanon's tourism sector will be greatly affected by higher temperatures, reduced agricultural output, and an increased frequency of extreme events, as the country's mild weather and services are major tourism attractions for markets like the GCC. The diagram of projected trends in emissions and warming is courtesy of the Climate Action Tracker. Artwork © OHK Consultants.
OHK went further to build a toolbox to support its unified global framework. This toolbox integrates a range of tools and methodologies to create a comprehensive and integrative sustainable tourism planning and recovery strategy. It provides a foundation for the methods and processes that a team implementing a strategy or plan can use to realize the framework. The toolbox includes tools for evaluating a destination's climate change performance and emissions, as well as methods to measure a country's competitiveness and the economic contribution of tourism under both climate change considerations and "do nothing" scenarios.
Simultaneously, the toolbox contains guidelines and resources that inform climate change mitigation and adaptation efforts and prioritize areas for conservation and management. It also assists in assessing the vulnerability of tourism destinations to climate change and guides adaptation measures. Furthermore, the toolbox includes resources to monitor and evaluate the sustainability of tourism destinations and businesses. Incorporating climate risk adaptation tools can further help tourism stakeholders identify risks, prioritize actions, and develop adaptation strategies. The toolbox also utilizes a multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) process, which can be used to prioritize climate change actions based on multiple criteria from a stakeholder pool, ensuring a wider net of opinions and the most effective and efficient actions are taken to achieve climate goals.
A holistic approach that overlays tools on top of a global framework for action can lead to the development and implementation of a robust and effective sustainable tourism planning and recovery strategy. This approach breaks down the complex challenges posed by climate change into building blocks within a framework, then uses individual tools to address each in an integrated way, tackling the myriad environmental, social, and economic issues comprehensively.
OHK is in the process of developing a capacity-building program to address the training needs of stakeholders in the tourism and climate change sectors, with the goal of helping them understand and apply various tools and frameworks to promote sustainable tourism. This program will take two distinct forms.
Firstly, OHK will offer a sustainability course designed to train individuals as qualified climate change assessors and problem solvers in tourism. This course will cover essential topics such as global baseline standards for sustainability in travel and tourism, performance evaluation and comparison of countries' climate protection, comprehensive methodologies for estimating national greenhouse gas emissions and removals, and the assessment of the conservation status of ecosystems. Participants will also learn about methodologies for conducting carbon footprint assessments, risk assessment, and adaptation strategies, as well as policy reform frameworks that promote sustainable development.
Secondly, OHK will develop a standardized exam to certify sustainability managers, targeting various industry stakeholders, such as government officials, tourism professionals, and local community activists. This certification will serve as a benchmark for demonstrating expertise in sustainable tourism practices, climate change mitigation, and adaptation strategies. By successfully completing the exam, certified sustainability managers will be equipped to implement and manage sustainable tourism initiatives based on the tools and frameworks covered in the training.
Through training and certification initiatives, OHK aims to empower stakeholders to effectively address the complex challenges posed by climate change within the tourism sector. By building their capacity to understand, apply, and integrate tools and frameworks, stakeholders will be better prepared to develop and implement sustainable tourism strategies and contribute to the global effort toward combating climate change.
To learn more about OHK’s work in sustainable strategy and climate change action, contact us.


